Stochastic drift
In probability theory, stochastic drift is the change of the average value of a stochastic (random) process. A related term is the drift rate which is the rate at which the average changes. This is in contrast to the random fluctuations about this average value. For example, the process which counts the number of heads in a series of  coin tosses has a drift rate of 1/2 per toss.
coin tosses has a drift rate of 1/2 per toss.
Contents |
Stochastic drifts in population studies
Longitudinal studies of secular events are frequently conceptualized as consisting of a trend component fitted by a polynomial, a cyclical component often fitted by an analysis based on autocorrelations or on a Fourier series, and a random component (stochastic drift) to be removed.
In the course of the time series analysis, identification of cyclical and stochastic drift components is often attempted by alternating autocorrelation analysis and differencing of the trend. Autocorrelation analysis helps to identify the correct phase of the fitted model while the successive differencing transforms the stochastic drift component into white noise.
Stochastic drift can also occur in population genetics where it is known as Genetic drift. A finite population of randomly-reproducing organisms would experience changes from generation to generation in the frequencies of the different genotypes. This may lead to the fixation of one of the genotypes, and even the emergence of a new species. In sufficiently small populations, drift can also neutralize the effect of deterministic natural selection on the population.
Stochastic drift in economics and finance
Time series variables in economics and finance — for example, stock prices, gross domestic product, etc. — generally evolve stochastically and frequently are non-stationary. They are typically modelled as either trend stationary or difference stationary. A trend stationary process {yt} evolves according to
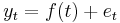
where t is time, f is a deterministic function, and et is a zero-long-run-mean stationary random variable. In this case the stochastic drift can be removed from the data by regressing 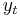 on
on 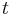 using a functional form coinciding with that of f, and retaining the residuals. In contrast, a unit root (difference stationary) process evolves according to
using a functional form coinciding with that of f, and retaining the residuals. In contrast, a unit root (difference stationary) process evolves according to
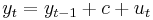
where 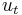 is a zero-long-run-mean stationary random variable; here c is a non-stochastic drift parameter: in the absence of the random shocks ut, the mean of the process would change by c per period. In this case the non-stationarity can be removed from the data by first differencing, and the differenced variable
is a zero-long-run-mean stationary random variable; here c is a non-stochastic drift parameter: in the absence of the random shocks ut, the mean of the process would change by c per period. In this case the non-stationarity can be removed from the data by first differencing, and the differenced variable 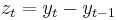 will have a mean of c and hence no drift.
will have a mean of c and hence no drift.
In the context of monetary policy, one policy question is whether a central bank should attempt to achieve a fixed growth rate of the price level from its current level in each time period, or whether to target a return of the price level to a predetermined growth path. In the latter case no price level drift is allowed away from the predetermined path, while in the former case any stochastic change to the price level permanently affects the expected values of the price level at each time along its future path. In either case the price level has drift in the sense of a rising expected value, but the cases differ according to the type of non-stationarity: difference stationarity in the former case, but trend stationarity in the latter case.
See also
References
- Krus, D.J., & Ko, H.O. (1983) Algorithm for autocorrelation analysis of secular trends. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 43, 821–828. (Request reprint).
- Krus, D. J., & Jacobsen, J. L. (1983) Through a glass, clearly? A computer program for generalized adaptive filtering. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 43, 149–154